Αρχείο:Convex outcome set of a multi-objective optimization problem.gif
Convex_outcome_set_of_a_multi-objective_optimization_problem.gif (360 × 392 εικονοστοιχεία, μέγεθος αρχείου: 906 KB, τύπος MIME: image/gif, κυκλικά επαναλαμβανόμενο, 99 καρέ, 4,9 s)
|
|
Αυτό το αρχείο και η περιγραφή του προέρχονται από το Wikimedia Commons. Οι πληροφορίες από την σελίδα περιγραφής του εκεί εμφανίζονται παρακάτω. |
The weighted-sum approach minimizes function 

where


such that


To have a convex outcome set, parameters 



Weights 


![{\displaystyle \omega _{1}\in [0;1]~}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/99c8913e84daf282e85b04849cc18cc14594dda7)

Σύνοψη
| ΠεριγραφήConvex outcome set of a multi-objective optimization problem.gif |
English: Weighted-sum approach is an easy method used to solve multi-objective optimization problem. It consists in aggregating the different optimization functions in a single function. However, this method only allows to find the supported solutions of the problem (i.e. points on the convex hull of the objective set). This animation shows that when the outcome set is convex, all efficient solutions can be found.
Français : La méthode des sommes pondérées est une méthode simple pour résoudre des problèmes d'optimisation multi-objectif. Elle consiste à aggréger l'ensemble des fonctions dans une seule fonction avec différents poids. Toutefois, cette méthode permet uniquement de trouver les solutions supportées (càd les points non-dominés appartenant à l'enveloppe convexe de l'espace d'arrivée). Cette animation montre qu'il est possible d'identifier toutes les solutions efficaces lorsque l'espace d'arrivée est convexe. |
| Ημερομηνία | |
| Πηγή | Έργο αυτού που το ανεβάζει |
| Δημιουργός | Guillaume Jacquenot |
Source code (MATLAB)
function MO_Animate(varargin)
% This function generates objective space images showing why
% sum-weighted optimizer can not find all non-dominated
% solutions for non convex objective spaces in multi-ojective
% optimization
%
% Guillaume JACQUENOT
if nargin == 0
Simu = 'Convex';
% Simu = 'NonConvex';
save_pictures = true;
interpreter = 'none';
end
switch Simu
case 'NonConvex'
a = 0.1;
b = 3;
stepX = 1/200;
stepY = 1/200;
case 'Convex'
a = 0.2;
b = 1;
stepX = 1/200;
stepY = 1/200;
end
[X,Y] = meshgrid( 0:stepX:1,-2:stepY:2);
F1 = X;
F2 = 1+Y.^2-X-a*sin(b*pi*X);
figure;
grid on;
hold on;
box on;
axis square;
set(gca,'xtick',0:0.2:1);
set(gca,'ytick',0:0.2:1);
Ttr = get(gca,'XTickLabel');
Ttr(1,:)='0.0';
Ttr(end,:)='1.0';
set(gca,'XTickLabel',[repmat(' ',size(Ttr,1),1) Ttr]);
Ttr = get(gca,'YTickLabel');
Ttr(1,:)='0.0';
Ttr(end,:)='1.0';
set(gca,'YTickLabel',[repmat(' ',size(Ttr,1),1) Ttr]);
if strcmp(interpreter,'none')
xlabel('f1','Interpreter','none');
ylabel('f2','Interpreter','none','rotation',0);
else
xlabel('f_1','Interpreter','Tex');
ylabel('f_2','Interpreter','Tex','rotation',0);
end
set(gcf,'Units','centimeters')
set(gcf,'OuterPosition',[3 3 3+6 3+6])
set(gcf,'PaperPositionMode','auto')
[minF2,minF2_index] = min(F2);
minF2_index = minF2_index + (0:numel(minF2_index)-1)*size(X,1);
O1 = F1(minF2_index)';
O2 = minF2';
[pF,Pareto]=prtp([O1,O2]);
fill([O1( Pareto);1],[O2( Pareto);1],repmat(0.95,1,3));
text(0.45,0.75,'Objective space');
text(0.1,0.9,'\leftarrow Optimal Pareto front','Interpreter','TeX');
plot(O1( Pareto),O2( Pareto),'k-','LineWidth',2);
plot(O1(~Pareto),O2(~Pareto),'.','color',[1 1 1]*0.8);
V1 = O1( Pareto); V1 = V1(end:-1:1);
V2 = O2( Pareto); V2 = V2(end:-1:1);
O1P = O1( Pareto);
O2P = O2( Pareto);
O1PC = [O1P;max(O1P)];
O2PC = [O2P;max(O2P)];
ConvH = convhull(O1PC,O2PC);
ConvH(ConvH==numel(O2PC))=[];
c = setdiff(1:numel(O1P), ConvH);
% Non convex
O1PNC = O1PC(c);
[temp, I1] = min(O1PNC);
[temp, I2] = max(O1PNC);
if ~isempty(I1) && ~isempty(I2)
plot(O1PC(c),O2PC(c),'-','color',[1 1 1]*0.7,'LineWidth',2);
end
p1 = (V2(1)-V2(2))/(V1(1)-V1(2));
hp = plot([0 1],[p1*(-V1(1))+V2(1) p1*(1-V1(1))+V2(1)]);
delete(hp);
Histo_X = [];
Histo_Y = [];
coeff = 0.02;
Sq1 = coeff *[0 1 1 0 0;0 0 1 1 0];
compt = 1;
for i = 2:1:length(V1)-1
if ismember(i,ConvH)
p1 = (V2(i+1)-V2(i-1))/(V1(i+1)-V1(i-1));
x_inter = 1/(1+p1^2)*(p1^2*V1(i)-p1*V2(i));
hp1 = plot([0 1],[p1*(-V1(i))+V2(i) p1*(1-V1(i))+V2(i)],'k');
% hp2 = plot([x_inter],[-x_inter/p1],'k','Marker','.','MarkerSize',8)
hp3 = plot([0 x_inter],[0 -x_inter/p1],'k-');
hp4 = plot([x_inter 1],[-x_inter/p1 -1/p1],'k--');
hp5 = plot(V1(i),V2(i),'ko','MarkerSize',10);
% Plot the square for perpendicular lines
alpha = atan(-1/p1);
Mrot = [cos(alpha) -sin(alpha);sin(alpha) cos(alpha)];
Sq_plot = repmat([x_inter;-x_inter/p1],1,5) + Mrot * Sq1;
hp7 = plot(Sq_plot(1,:),Sq_plot(2,:),'k-');
Histo_X = [Histo_X V1(i)];
Histo_Y = [Histo_Y V2(i)];
hp6 = plot(Histo_X,Histo_Y,'k.','MarkerSize',10);
w1 = p1/(p1-1);
w2 = 1-w1;
Fweight_sum = V1(i)*w1+w2*V2(i);
Fweight_sum = floor(1e3*Fweight_sum )/1e3;
w1 = floor(1000*w1)/1e3;
str1 = sprintf('%.3f',w1);
str2 = sprintf('%.3f',1-w1);
str3 = sprintf('%.3f',Fweight_sum);
if (strcmp(str1,'0.500')||strcmp(str1,'0,500')) && strcmp(Simu,'NonConvex')
disp('Two solutions');
end
title(['\omega_1 = ' str1 ' & \omega_2 = ' str2 ' & F = ' str3],'Interpreter','TeX');
axis([0 1 0 1]);
file = ['Frame' num2str(1000+compt)];
if save_pictures
saveas(gcf, file, 'epsc');
end
compt = compt +1;
pause(0.001);
delete(hp1);
delete(hp3);
delete(hp4);
delete(hp5);
delete(hp6);
delete(hp7);
end
end
disp(['Number of frames :' num2str(length(V1))]);
return;
function [A varargout]=prtp(B)
% Let Fi(X), i=1...n, are objective functions
% for minimization.
% A point X* is said to be Pareto optimal one
% if there is no X such that Fi(X)<=Fi(X*) for
% all i=1...n, with at least one strict inequality.
% A=prtp(B),
% B - m x n input matrix: B=
% [F1(X1) F2(X1) ... Fn(X1);
% F1(X2) F2(X2) ... Fn(X2);
% .......................
% F1(Xm) F2(Xm) ... Fn(Xm)]
% A - an output matrix with rows which are Pareto
% points (rows) of input matrix B.
% [A,b]=prtp(B). b is a vector which contains serial
% numbers of matrix B Pareto points (rows).
% Example.
% B=[0 1 2; 1 2 3; 3 2 1; 4 0 2; 2 2 1;...
% 1 1 2; 2 1 1; 0 2 2];
% [A b]=prtp(B)
% A =
% 0 1 2
% 4 0 2
% 2 2 1
% b =
% 1 4 7
A=[]; varargout{1}=[];
sz1=size(B,1);
jj=0; kk(sz1)=0;
c(sz1,size(B,2))=0;
bb=c;
for k=1:sz1
j=0;
ak=B(k,:);
for i=1:sz1
if i~=k
j=j+1;
bb(j,:)=ak-B(i,:);
end
end
if any(bb(1:j,:)'<0)
jj=jj+1;
c(jj,:)=ak;
kk(jj)=k;
end
end
if jj
A=c(1:jj,:);
varargout{1}=kk(1:jj);
else
warning([mfilename ':w0'],...
'There are no Pareto points. The result is an empty matrix.')
end
return;
diagram δημιουργήθηκε με MATLAB.
Αδειοδότηση
Εγώ, ο κάτοχος των πνευματικών δικαιωμάτων αυτού του έργου, το δημοσιεύω δια του παρόντος υπό τις εξής άδειες χρήσης:

|
Παραχωρείται η άδεια προς αντιγραφή, διανομή και/ή τροποποίηση αυτού του εγγράφου υπό τους όρους της Άδειας Ελεύθερης Τεκμηρίωσης GNU, Έκδοση 1.2 ή οποιασδήποτε νεότερης έκδοσης δημοσιευμένης από το Ίδρυμα Ελεύθερου Λογισμικού· χωρίς Απαράλαχτους Τομείς, χωρίς Κείμενα Εξωφύλλου, και χωρίς Κείμενα Οπισθοφύλλου. Αντίγραφο της άδειας περιλαμβάνεται στην σελίδα με τίτλο GNU Free Documentation License.http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.htmlGFDLGNU Free Documentation Licensetruetrue |
Αυτό το αρχείο έχει αδειοδοτηθεί υπό τις Creative Commons Αναφορά προέλευσης 3.0 Unported, 2.5 Generic, 2.0 Generic και 1.0 Generic άδειες χρήσης.
- Είστε ελεύθερος:
- να μοιραστείτε – να αντιγράψετε, διανέμετε και να μεταδώσετε το έργο
- να διασκευάσετε – να τροποποιήσετε το έργο
- Υπό τις ακόλουθες προϋποθέσεις:
- αναφορά προέλευσης – Θα πρέπει να κάνετε κατάλληλη αναφορά, να παρέχετε σύνδεσμο για την άδεια και να επισημάνετε εάν έγιναν αλλαγές. Μπορείτε να το κάνετε με οποιοδήποτε αιτιολογήσιμο λόγο, χωρίς όμως να εννοείται με οποιονδήποτε τρόπο ότι εγκρίνουν εσάς ή τη χρήση του έργου από εσάς.
- παρόμοια διανομή – Εάν αλλάξετε, τροποποιήσετε ή δημιουργήσετε πάνω στο έργο αυτό, μπορείτε να διανείμετε αυτό που θα προκύψει μόνο υπό τους όρους της ίδιας ή συμβατής άδειας με το πρωτότυπο.
Μπορείτε να επιλέξετε την άδεια της προτίμησής σας.
Λεζάντες
Δεν ορίστηκε λεζάντα
Items portrayed in this file
απεικονίζει
some value
8 Μαρτίου 2009
image/gif
checksum Αγγλικά
7479bfd15df7aaec6e8b9b4ad4e8743d8795356c
data size Αγγλικά
928.183 Byte
4,94999999999999 δευτερόλεπτο
392 εικονοστοιχείο
360 εικονοστοιχείο
Ιστορικό αρχείου
Κλικάρετε σε μια ημερομηνία/ώρα για να δείτε το αρχείο όπως εμφανιζόταν εκείνη τη στιγμή.
| Ώρα/Ημερομ. | Μικρογραφία | Διαστάσεις | Χρήστης | Σχόλια | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| τελευταία | 16:55, 8 Μαρτίου 2009 | 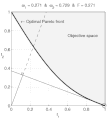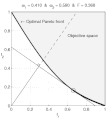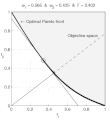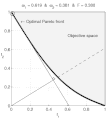 | 360 × 392 (906 KB) | Gjacquenot | {{Information |Description={{en|1=Weighted-sum approach is an easy method used to solve multi-objective optimization problem. It consists in aggregating the different optimization functions in a single function. However, this method only allows to find th |
Συνδέσεις αρχείου
Τα παρακάτω λήμματα συνδέουν σε αυτό το αρχείο:
Καθολική χρήση αρχείου
Τα ακόλουθα άλλα wiki χρησιμοποιούν αυτό το αρχείο:
- Χρήση σε it.wikipedia.org
